Diagnostics
Rapid, Sensitive POC Diagnostics
Timely and accurate identification of the causal pathogen is critical in providing an appropriate response, treatment and patient care for any infectious disease. Linking infectious agent diagnostics to clinical decision-making at the point-of-care (POC), requires a fast, highly sensitive and simple-to-use method that complements the clinical infrastructure and workflow across a diverse range of developed and underdeveloped patient care settings.
Throughout history, global human health has been seriously impacted by emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. In the 14th century the Black Death, caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, is estimated to have killed 30-60% of Europe's total population, while the Spanish Flu pandemic claimed more than 50 million lives from 1918-20, HIV, initially discovered in 1981, still claims approximately one million lives globally each year, and the 2013-15 outbreak of Ebola in Western Africa infected more than 28,000 people.
More recently the 2015-16 Zika virus outbreak infected over 500,000 in the Americas. While Zika infection is typically a self-limiting disease with moderate symptoms it is also associated with the development of neurological complications including microcephaly in newborns from women infected during pregnancy and Guillain-Barre Syndrome in some adults. In addition, more than one-third of the world's population currently lives in areas at risk for infection by the related flavivirus, dengue, which is a leading cause of illness and death in the tropics and subtropics. As many as 400 million people are infected yearly putting them at risk for more severe forms of the disease including dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can be fatal.
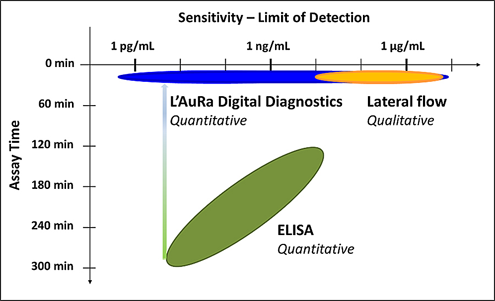
The current diagnostic focus of Arisan is the development of novel, rapid and sensitive POC diagnostic tests that enable early stage detection of dengue and Zika virus infections. Arisan has identified complementary antibody pairs that provide sensitive and selective detection of dengue and Zika biomarkers. In collaboration with LamdaGen Corporation and in association with the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID), highly sensitive, selective and quantitative rapid, field deployable diagnostic tests are currently in development. The POC / mobile L' AuRa Digital platform-based diagnostics exploit LamdaGen's patented nano-based Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR) biosensors to provide significant performance advantages over existing diagnostic technologies (ELISAs and LFAs), including speed, simplicity and sensitivity (Figure 1).